√99以上 gases responsible for greenhouse effect on earth 275825-Which gas is responsible for greenhouse effect
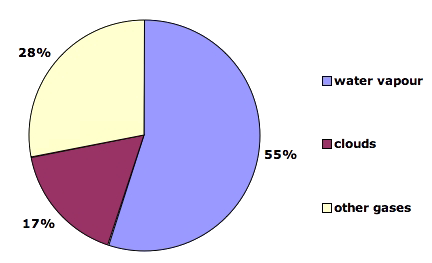
You can think of greenhouse gases as sort of a "blanket" for infrared radiation they keep the Earth's surface and lower layers of the atmosphere warmer, and the upper layers colder, than if the greenhouse gases were not there About 8090% of the Earth's natural greenhouse effect is due to water vapor and cloudsWater vapor is known to be Earth's most abundant greenhouse gas, but the extent of its contribution to global warming has been debated Using recent NASA satellite data, researchers have estimated more precisely than ever the heattrapping effect of water in the air, validating the role of the gas as a critical component of climate change The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some of
Climate Explained Why Carbon Dioxide Has Such Outsized Influence On Earth S Climate
Which gas is responsible for greenhouse effect
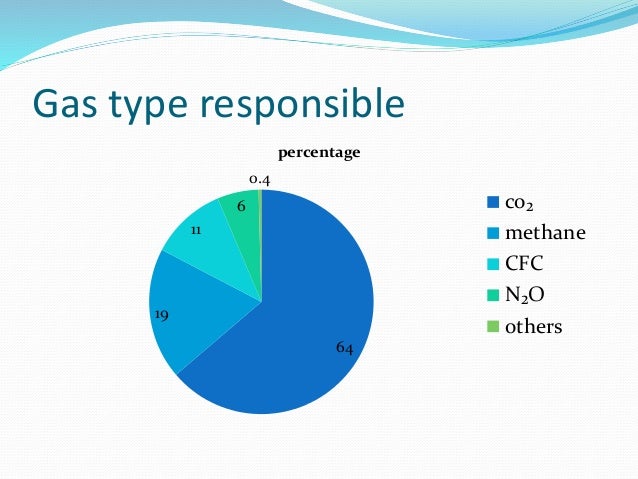
Which gas is responsible for greenhouse effect-Fluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6 Even though greenhouse gases don't make a hard surface like the glass of a greenhouse, but because they have a similar effect in keeping our planet warm, the term "Greenhouse Effect" is a good description The greenhouse effect keeps the temperatures on our planet mild and suitable for living things Greenhouse gases (GHG) include carbon




Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society
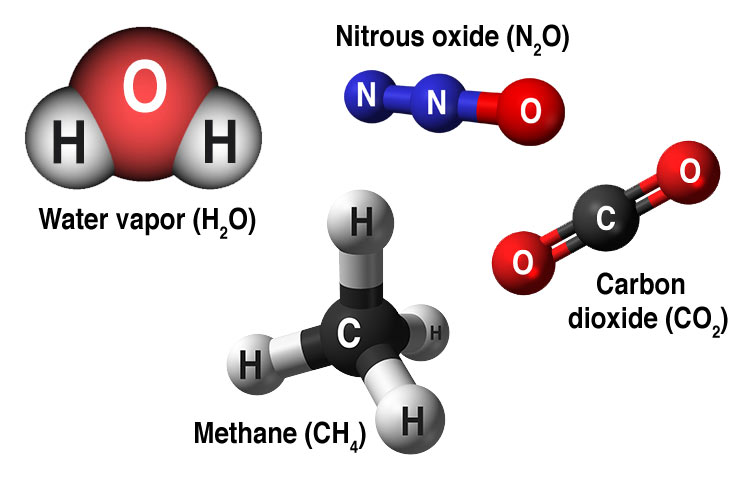
The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, nitrous oxides, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) On Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouse Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric CO 2The greenhouse effect and carbon dioxide Wenyi Zhong and Joanna D Haigh and the Greenhouse Effect The Earth is bathed in radiation from the Sun, wellmixed greenhouse gases are included with concentrations for CO 2 of 3ppmv, CH 4 176ppmv and N 2By their percentage contribution to the greenhouse effect on Earth the four major gases are Atmospheric gases only absorb some wavelengths of energy but are transparent to others The absorption patterns of water vapor (blue peaks) and carbon
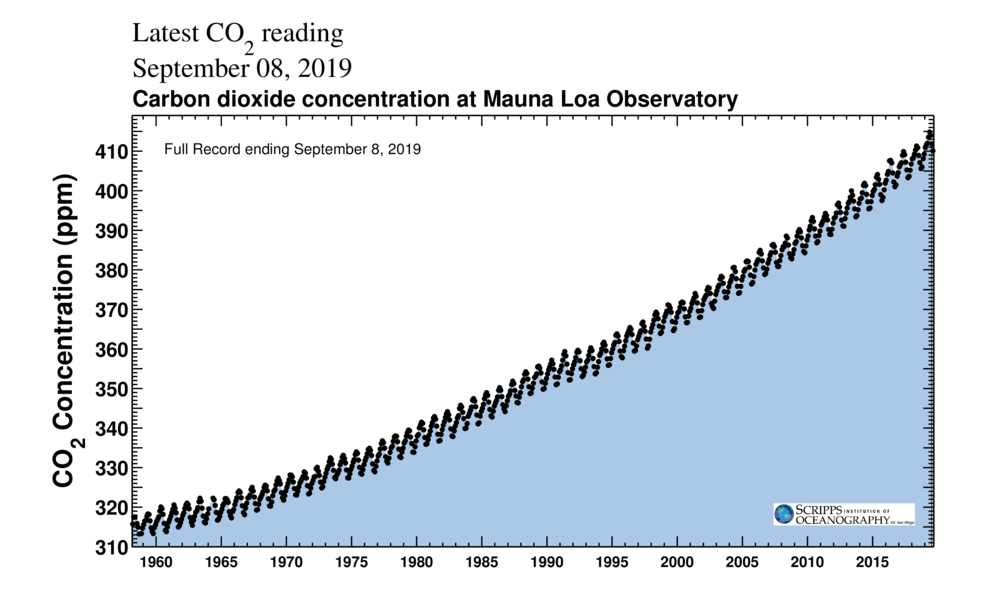
Carbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activitiesIn 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and All gases whose molecules have three or more atoms are greenhouse gases—carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), water vapor (H 2 O), and methane (CH 4) are important greenhouse gases that have maintained Earth's warm temperature for billions of years Source Intergovernmental Panel on Climate ChangeThere are five such gases rising concentration of which has been implicated in causing noticeable rise in the mean global temperatures These gases are carbon dioxide, methane, chlorofluorocarbons, nitrogen oxide and water vapours
The greenhouse effect is a natural process responsible for keeping the earth at the temperature needed to sustain life Acting just like the glass walls of a greenhouse, gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap the sun's heat in the atmosphere and prevent it It has long been accepted that the "greenhouse effect", where the atmosphere readily transmits short wavelength incoming solar radiation but selectively absorbs long wavelength outgoing radiation emitted by the earth, is responsible for warming the earth from the 255K effective earth temperature, without atmospheric warming, to the current average temperature Human activities and the greenhouse effect Human activities are increasing the amount of some greenhouse gases in the atmosphere For




Climate Explained Why Carbon Dioxide Has Such Outsized Influence On Earth S Climate
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16185712/Screen_Shot_2019_04_23_at_5.44.31_PM.png)



Climate Change Animation Shows Us Leading The World In Carbon Emissions Vox
Gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include Water vapor The most abundant greenhouse gas, but importantly, it acts as a feedback to the climateLikewise, methane is responsible for a large portion of recent warming despite having a GWP much lower than several other greenhouse gases because emissions have increased drastically * No single lifetime can be given for carbon dioxide because it The greenhouse gases causing the greenhouse effect work as a barrierfilter for the atmosphere The sun radiates solar energy on the earth and greenhouse gases make sure that 45% of these harmful solar radiations do not reach the surface of the planet by bouncing back most of the damaging UV radiation back into space Greenhouse Gases Maintain



Greenhouse Gases




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere, the Earth would be much colder on average than it is now Greenhouse gases absorb energy Human activities responsible for rapid increase in Earth's heat Increases in greenhouse gases, decreases in aerosols and polar seaice, are major factors A new study by Princeton University and NOAA researchers has found clear evidence of human influence on Earth's climate in the past two decades of satellite measurements Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect helps stabilize Earth's atmosphere Remove carbon dioxide, and the terrestrial greenhouse effect would collapse Without carbon dioxide, Earth's surface would be some 33 °C (59 °F) cooler




Food Production Is Responsible For One Quarter Of The World S Greenhouse Gas Emissions Our World In Data




Global Warming Greenhouse Gas Models For Kids
Dumping – Human waste is made up of high levels of carbon dioxide and methane gas which disenables the natural greenhouse effect's ability to transfer energy normally Artificial power – Motorized and electrical processes are another harmful contributor towards raising the bar of the new greenhouse gas effect By increasing the heat in the atmosphere, greenhouse gases are responsible for the greenhouse effect, which ultimately leads to global warming RelatedCarbon dioxide, methane, and halocarbons are greenhouse gases that absorb a wide range of energy—including infrared energy (heat) emitted by the Earth—and then reemit it The reemitted energy travels out in all directions, but some returns to Earth, where it heats the surface




Greenhouse Gas
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/assets/4191473/Human_Fingerprints.jpg)



How Do We Know Humans Are Causing Global Warming Vox
Most of these humancaused (anthropogenic) greenhouse gas emissions were carbon dioxide (CO2) from burning fossil fuels Concentrations of CO2 in the atmosphere are naturally regulated by many processes that are part of the global carbon cycle Greenhouse gases Their impact on climate change Terry Gibb, Michigan State University Extension Many scientists are predicting the Earth is heading toward a global warming danger zone and humans are responsible for most of it by upsetting the balance in the natural ecosystem Climate change has been debated for a while on The "natural" greenhouse gases The two main gases responsible for the greenhouse effect (and not noly its recent increase) are Water vapour (H2O), carbon dioxyde (CO2) There are others such gases, and even many others Some of them are "natural", which means that they were present in the atmosphere before the apparition of men, and




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Ozcoasts




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
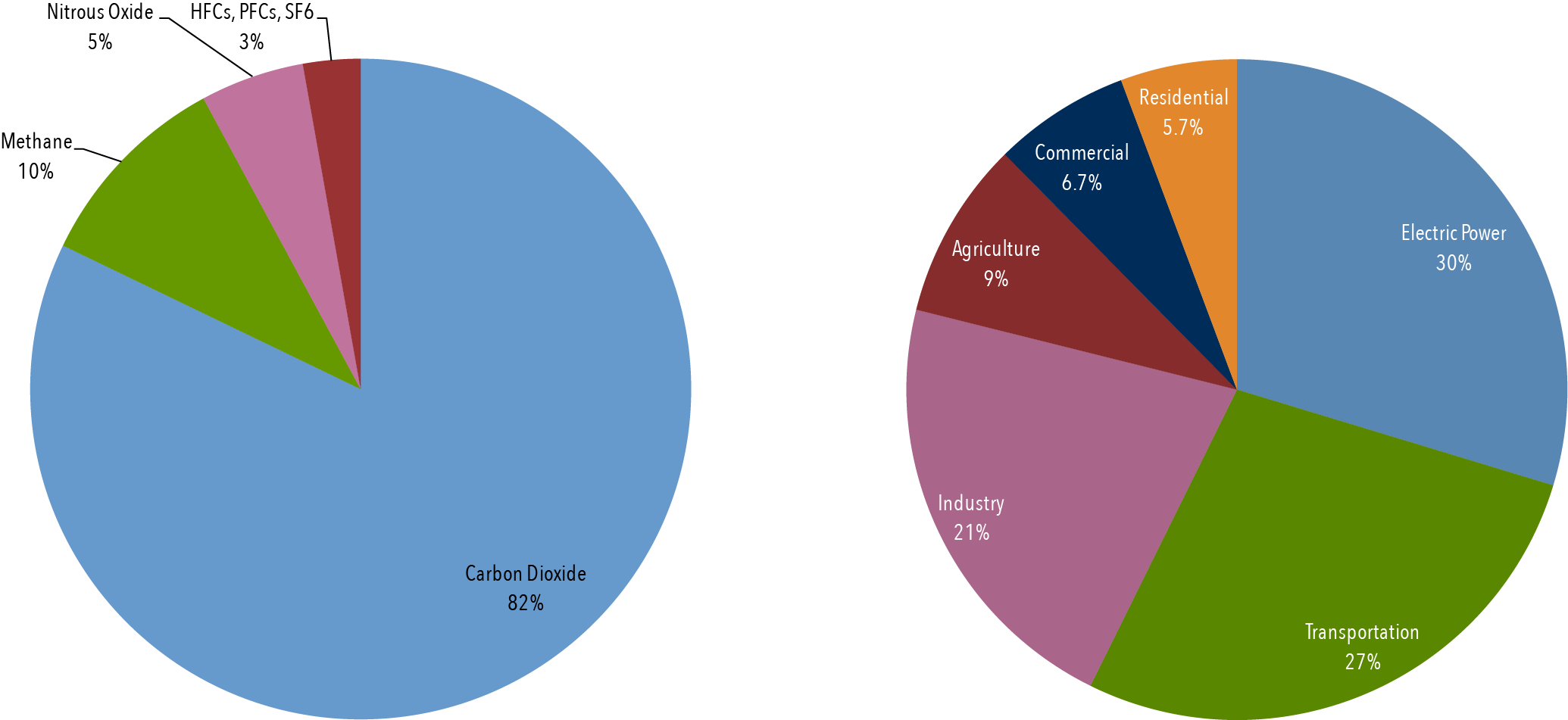
An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percentThe major types of emissions from the greenhouse gases released by people's simple everyday activities are Carbon dioxide (54%) Carbon dioxide is the leading culprit of greenhouse gas Carbon dioxide not only contributes over half of the atmospheric pollution creating climate change, but is the easiest gas emission culprit to avoidThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gas es—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science
This article tries to answer a question about the greenhouse effect "Greenhouse gases prevent the infrared rays from leaving the Earth's atmosphere, but why do they not prevent additional solar radiation from entering the atmosphere?" The key is the different wavelength (or different frequency) of solar light and infrared light Let's have a look at the greenhouse effect In the wake of a rapidly changing climate, the topic of the greenhouse effect is now one of the most debatable one in the global community Whereas a group of scholars finds it a sustaining danger to human life, other groups claim it to be one of the crucial phenomena to sustain life on earth Our readers should have a better idea regarding the greenhouse phenomenon Venus Greenhouse Effect You might be surprised to know that Venus is the hottest planet in the Solar System With a global temperature



Atmo336 Spring 21
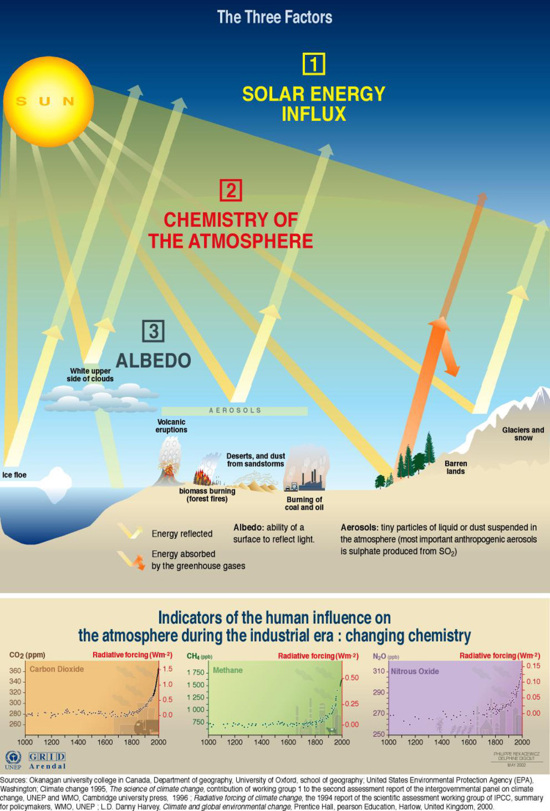



Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal
The strength of this effect depends upon the atmosphere's temperature and the amount of greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere The primary greenhouse gases known are water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ozone (O3) This paragraph has answered the question What is a greenhouse effect short answer? Bottom line An environmental scientist explains why carbon dioxide – CO2 – has such a big effect on Earth's atmosphere and the greenhouse effect Share Tweet The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), methane (CH 4 ), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3 ), and fluorinated gases




Noaa Index Tracks How Greenhouse Gas Pollution Amplified Global Warming In Welcome To Noaa Research
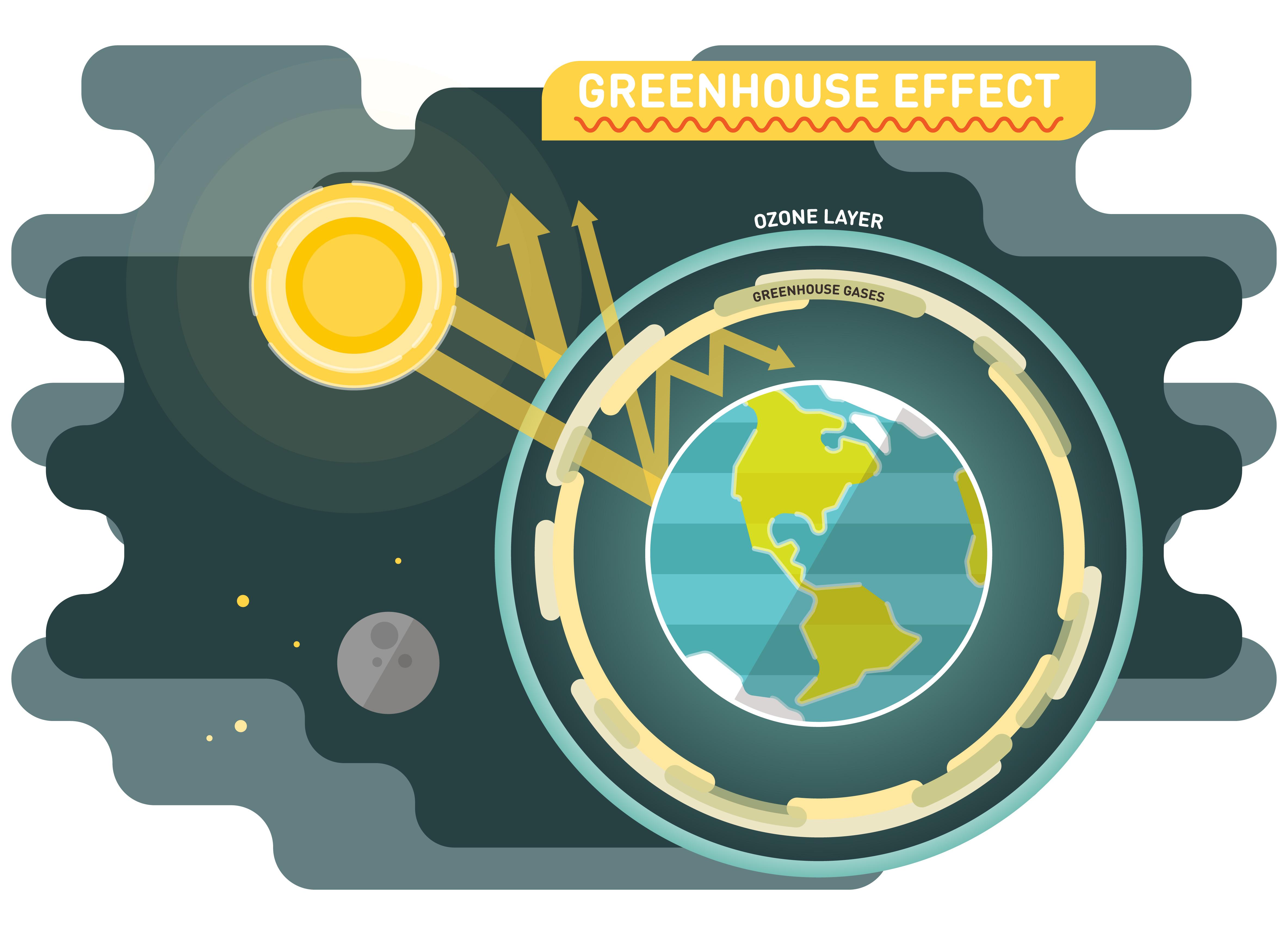



Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate
The greenhouse effect refers to the ability of the atmosphere to trap the sun's heat, increasing the temperature of the planet When the sun's energy reaches Earth, the atmosphere absorbs some of it on the way down, and then absorbs more when that energy reflects back off the surface during the day Greenhouse gases keep our planet livable by holding onto some of Earth's heat energy so that it doesn't all escape into space This heat trapping is known as the greenhouse effect Just as too little greenhouse gas makes Earth too cold, too much greenhouse gas makes Earth too warm Over the last century, humans have burned coal, oil, and




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Greenhouse Effect National Geographic Society




5 Notorious Greenhouse Gases Britannica




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




List The Gases Which Are Responsible For Greenhouse Effect
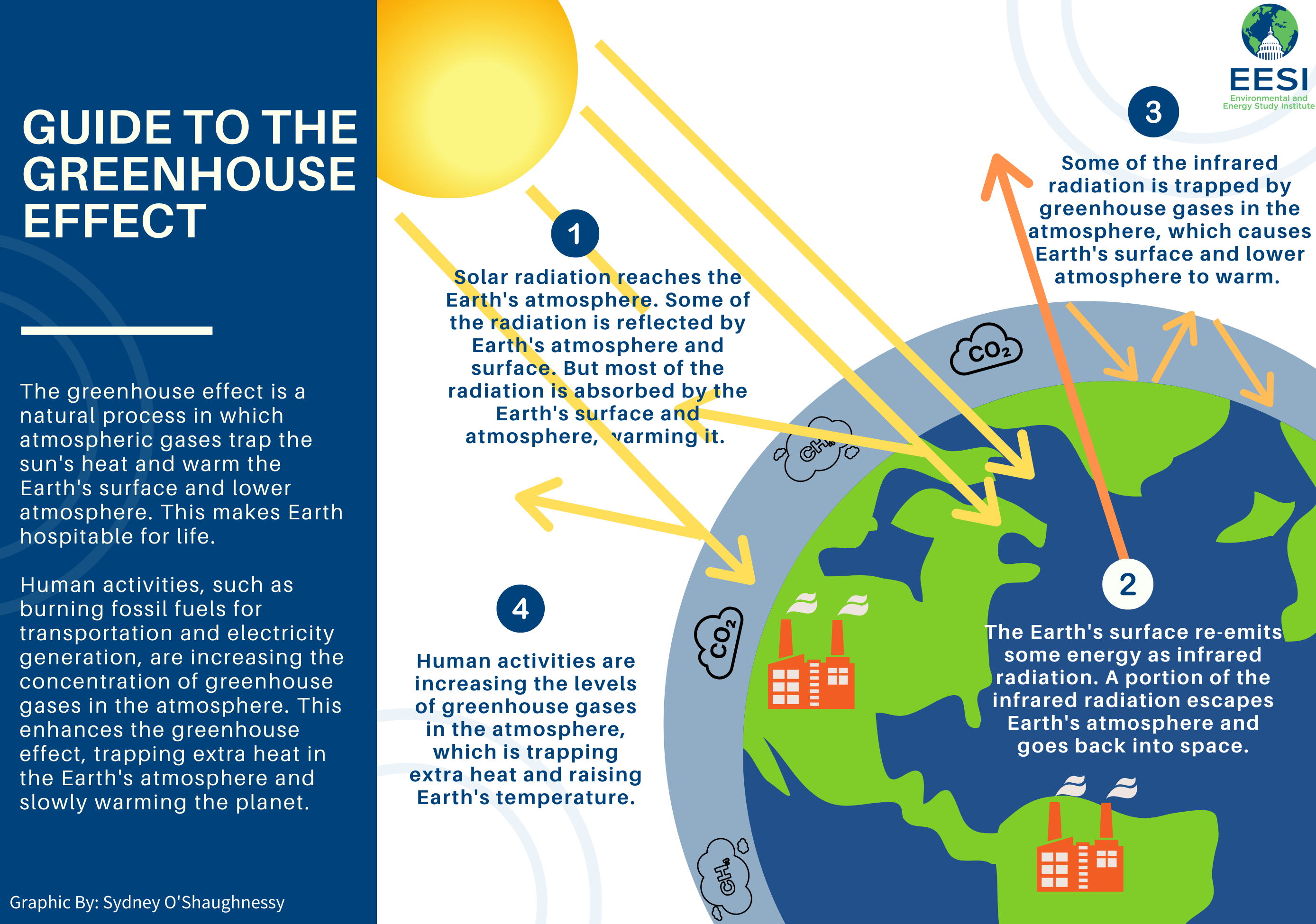



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi



Greenhouse Gases



Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




We Should Discuss Soil As Much As We Talk About Coal Bill Gates




Causes Of Global Warming How Scientists Know That Humans Are Responsible Yale Climate Connections



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici



Green House Effect



Climate Basics For Kids Center For Climate And Energy Solutions




Oil And Gas May Be A Far Bigger Climate Threat Than We Knew The New York Times




Tourism Responsible For 8 Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Study Finds Carbon Brief




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Explainer Co2 And Other Greenhouse Gases Science News For Students



1




The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Radiation From The Sun Easily Penetrates The Layer Of Gases Surrounding The Earth The Atmosphere Some Of This Ppt Download
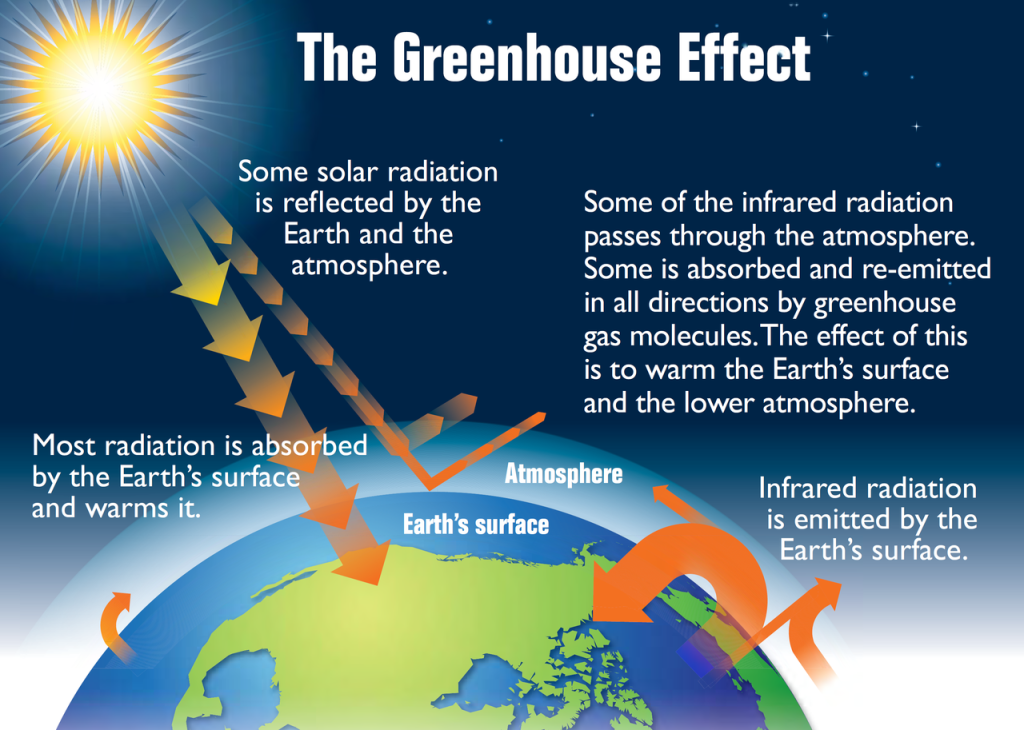



How Does The Greenhouse Effect Keep The Earth Warm Socratic




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering




Greenhouse Effect An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




Cows Methane And Climate Change Let S Talk Science
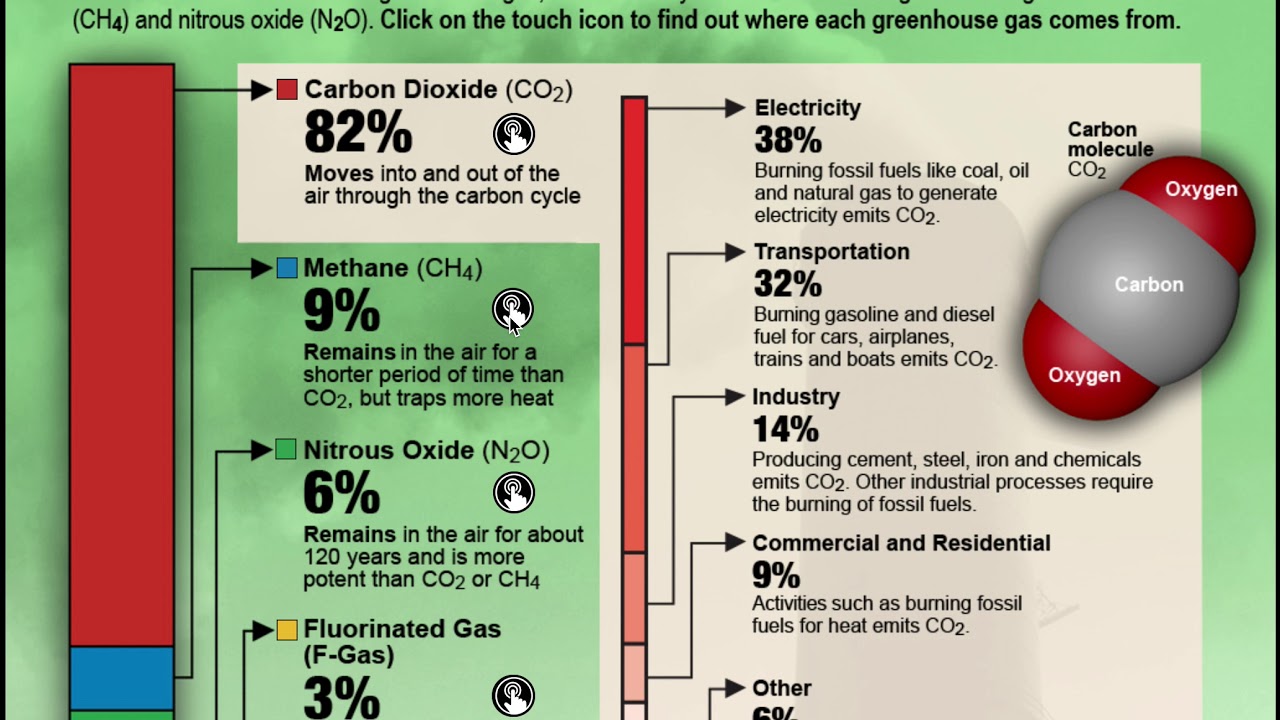



What Are Greenhouse Gases And Where Do They Come From Kqed




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases




Causes Of The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future




The Greenhouse Effect World101




Greenhouse Gas Emissions By Country And Sector Infographic News European Parliament
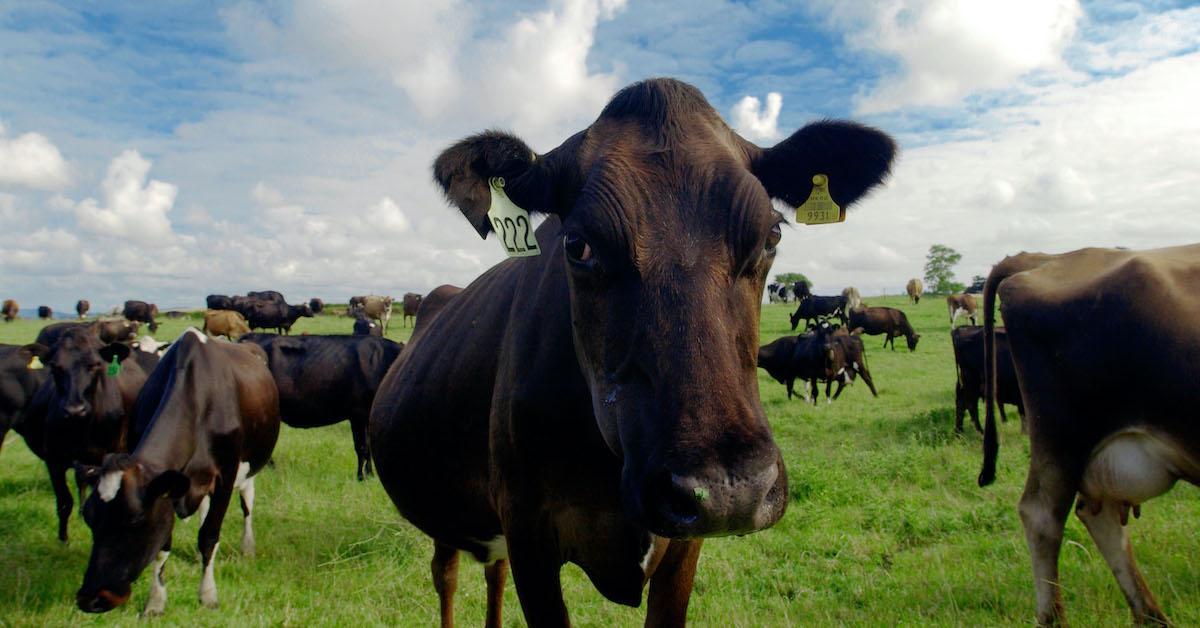




Why The Greenhouse Effect Is Important How It Affects The Climate




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
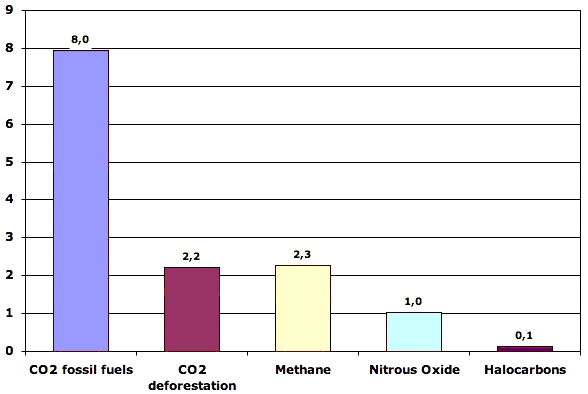



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia
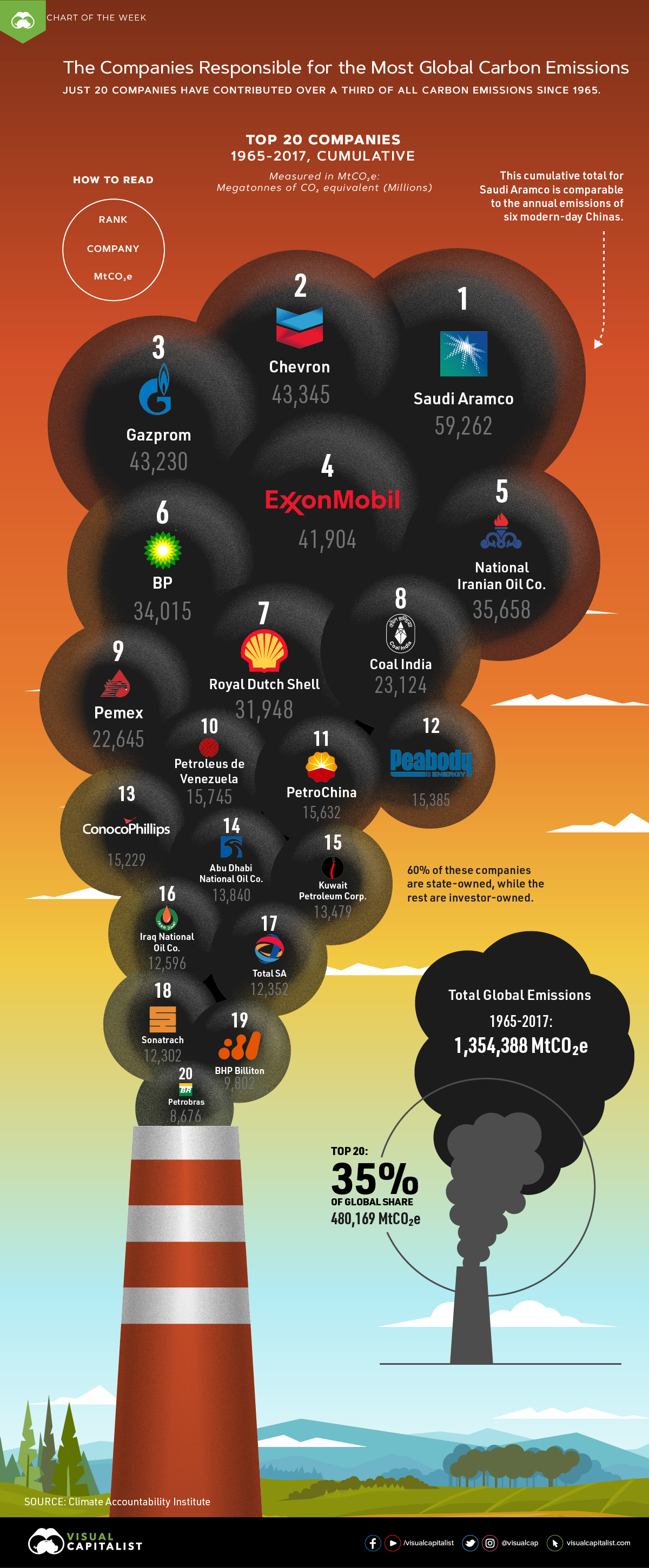



Which Companies Are Responsible For The Most Carbon Emissions



1




Engineering The Earth To Fight Climate Change Science In The News
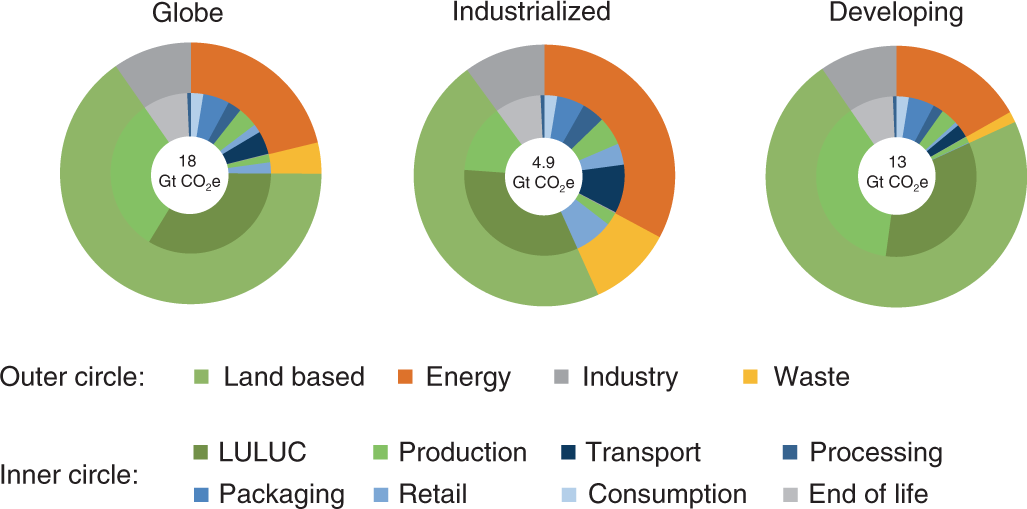



Food Systems Are Responsible For A Third Of Global Anthropogenic Ghg Emissions Nature Food




Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Data Us Epa



Humans And The Greenhouse Effect Climate Institute



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate




Carbon Intensive Industries The Industry Sectors That Emit The Most Carbon Eco Warrior Princess
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/16185122/gw_graphic_pie_chart_co2_emissions_by_country_2015.png)



Climate Change Animation Shows Us Leading The World In Carbon Emissions Vox



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
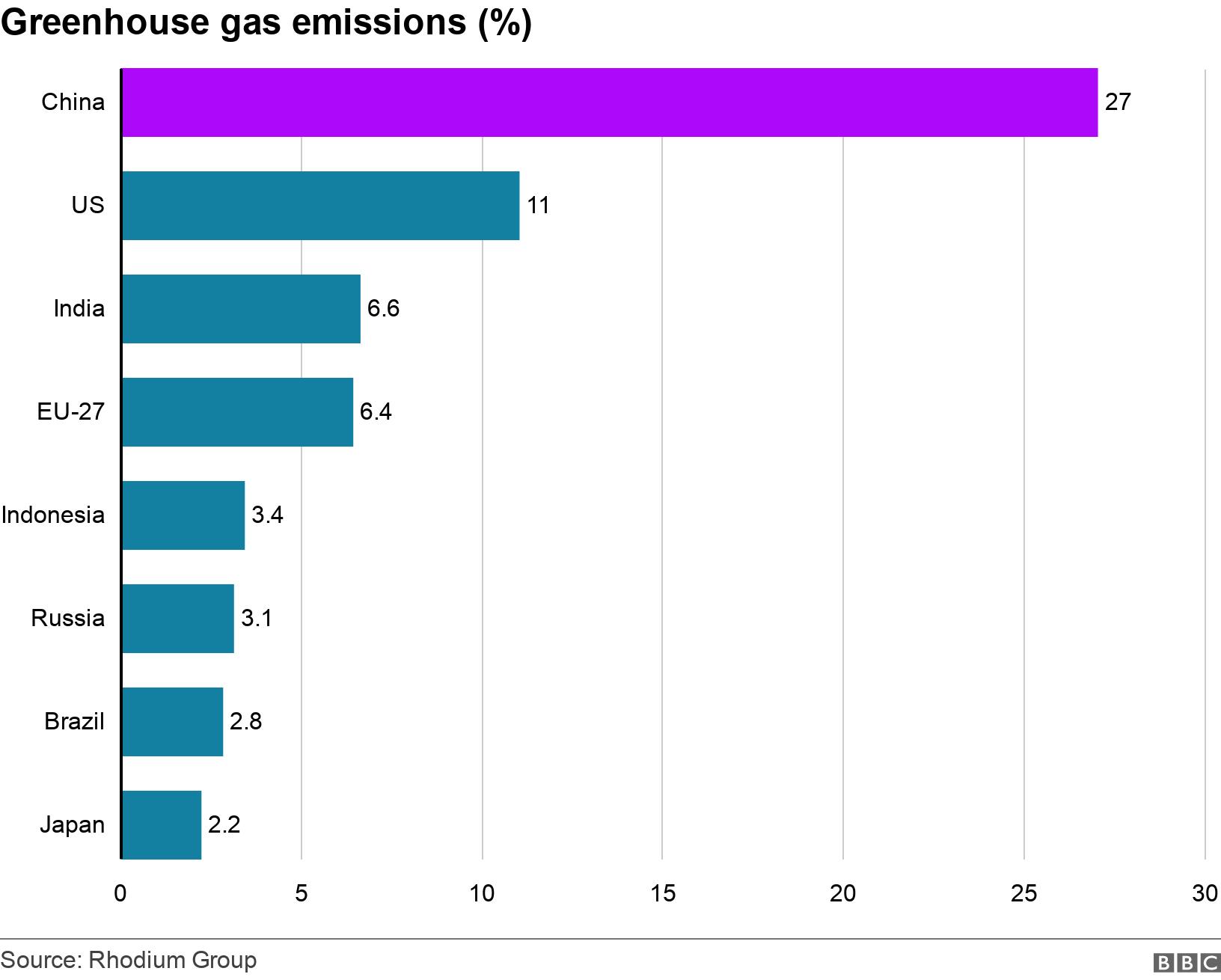



Report China Emissions Exceed All Developed Nations Combined c News




Greenhouse Gases American Chemical Society




Which Nations Are Most Responsible For Climate Change Environment Theguardian Com




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
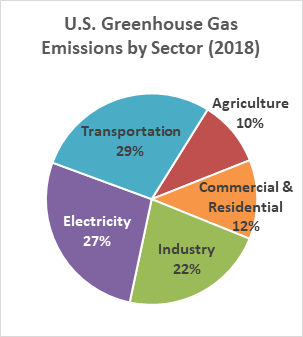



Global Warming Climate Change Frequently Asked Questions Faq Eesi
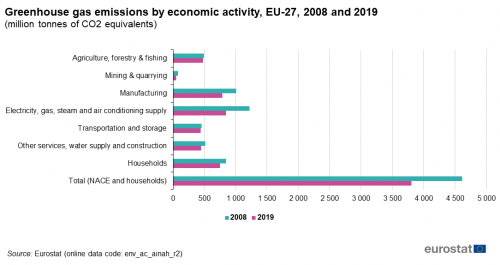



Greenhouse Gas Emission Statistics Air Emissions Accounts Statistics Explained




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Are Humans Causing Or Contributing To Global Warming Noaa Climate Gov




Rising Emissions Drive Greenhouse Gas Index Increase Welcome To Noaa Research
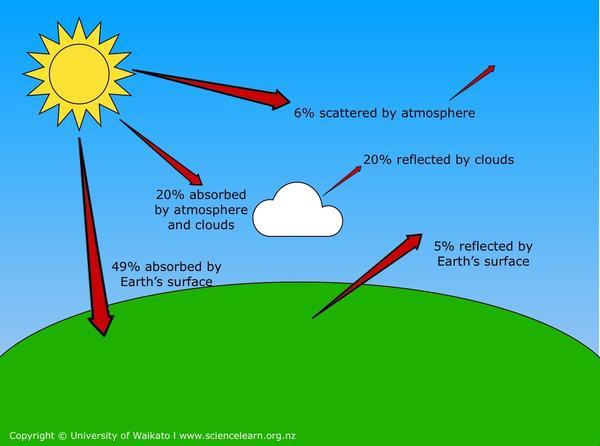



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub




Which Two Gases Are Most Responsible For Greenhouse Effect
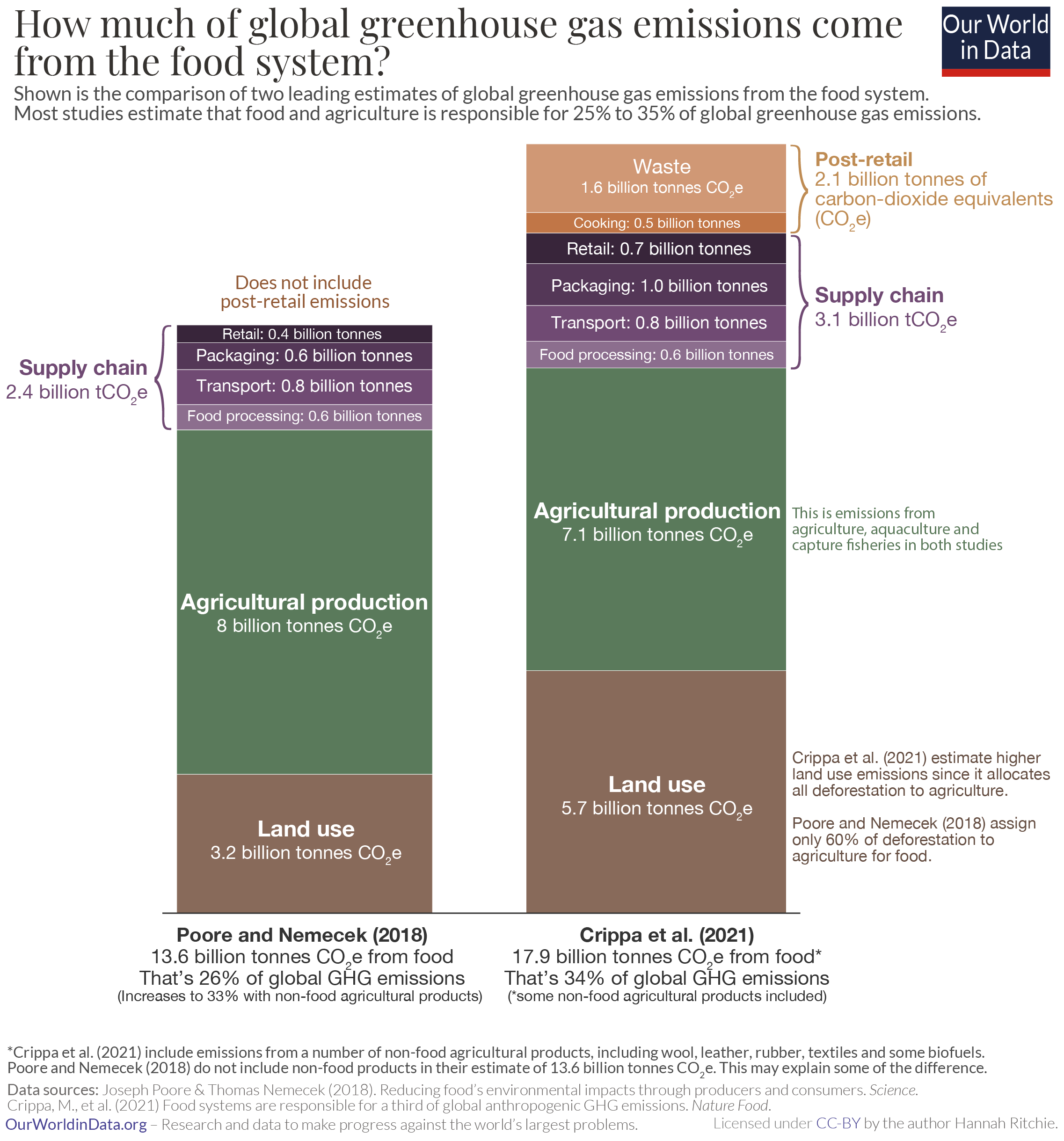



How Much Of Global Greenhouse Gas Emissions Come From Food Our World In Data



Emissions By Sector Our World In Data




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa



Carbon Dioxide
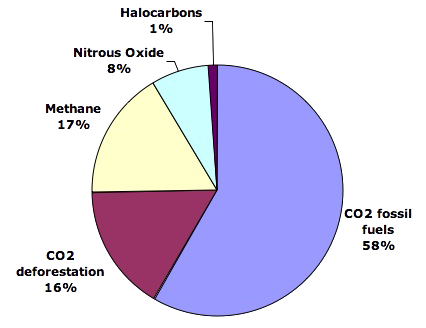



What Gases Are Greenhouse Gases Jean Marc Jancovici




The Perks Of Greenhouse Effect Top 5 Advantages Of Greenhouse Gases By Ameelia Black Medium




Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know




How Does Earth S Greenhouse Effect Work Saving Earth Encyclopedia Britannica




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa




Who Is Mainly Responsible For Greenhouse Gas Emissions Harvest Harmonics




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa




Greenhouse Gases Are Rapidly Changing The Atmosphere Climate Central
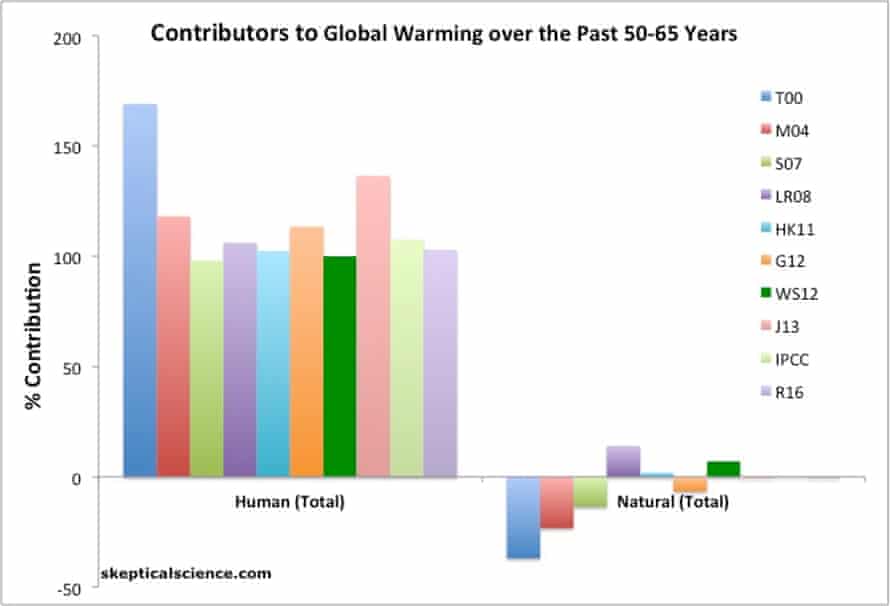



Study Humans Have Caused All The Global Warming Since 1950 Climate Crisis The Guardian




Global Warming Causes And Effects Global Warming Facts Effects Of Global Warming Global Warming Climate Change




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
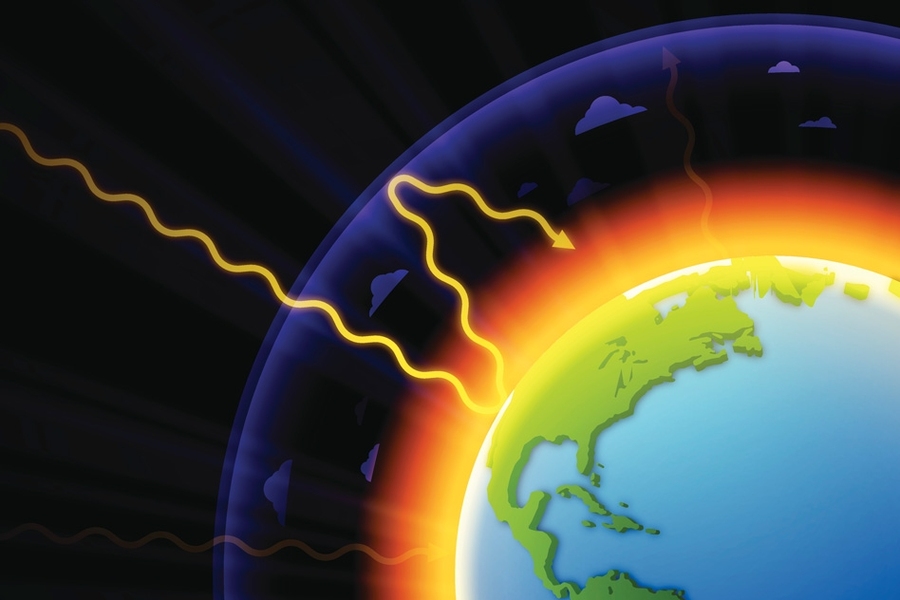




Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology
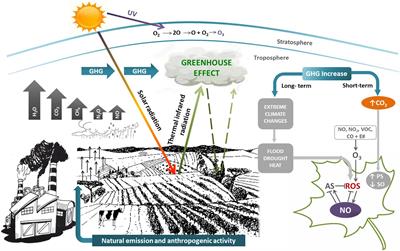



Frontiers Climate Change And The Impact Of Greenhouse Gasses Co2 And No Friends And Foes Of Plant Oxidative Stress Plant Science



Simple




1zrlfbmrqd Vwm
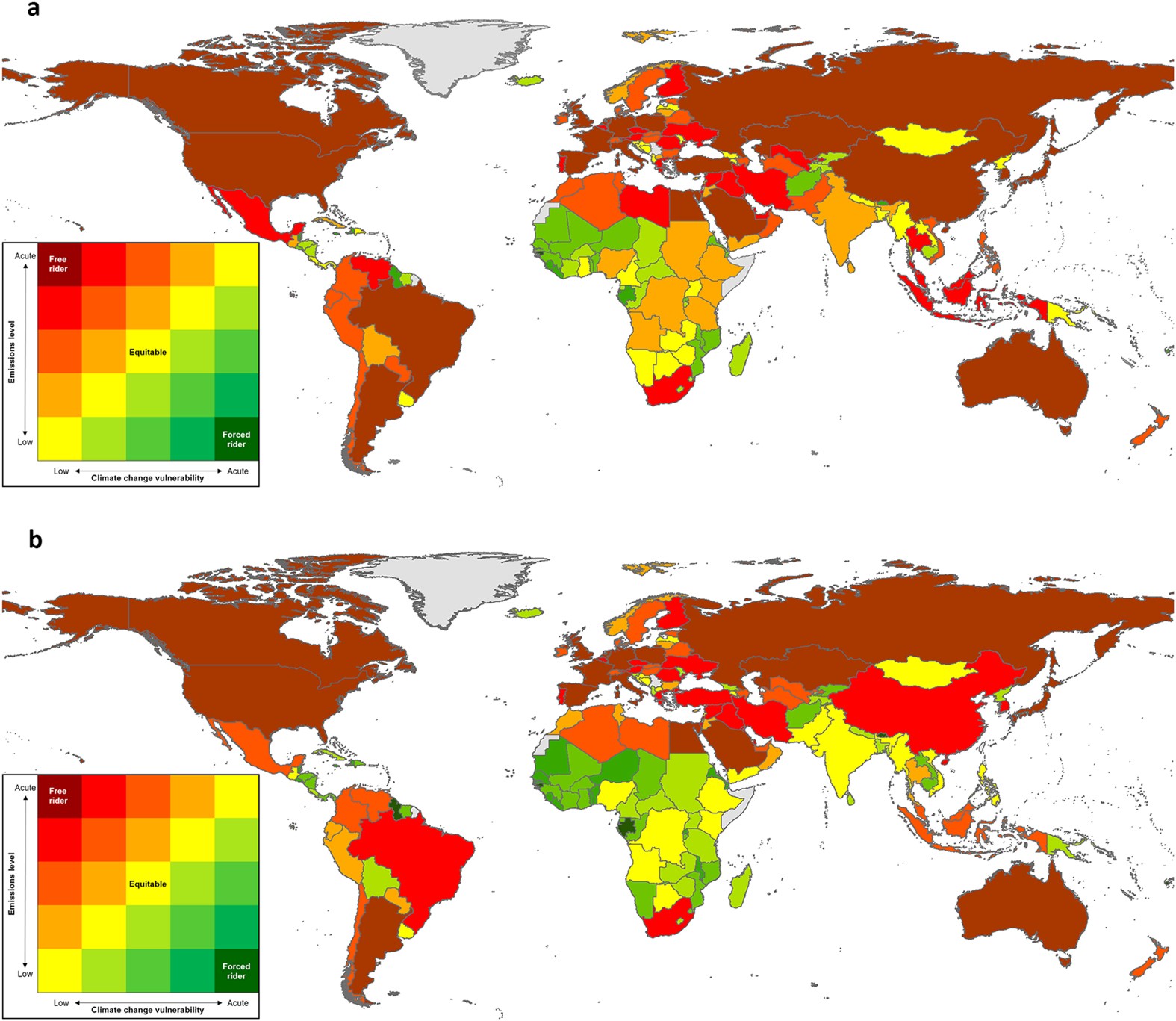



Global Mismatch Between Greenhouse Gas Emissions And The Burden Of Climate Change Scientific Reports




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
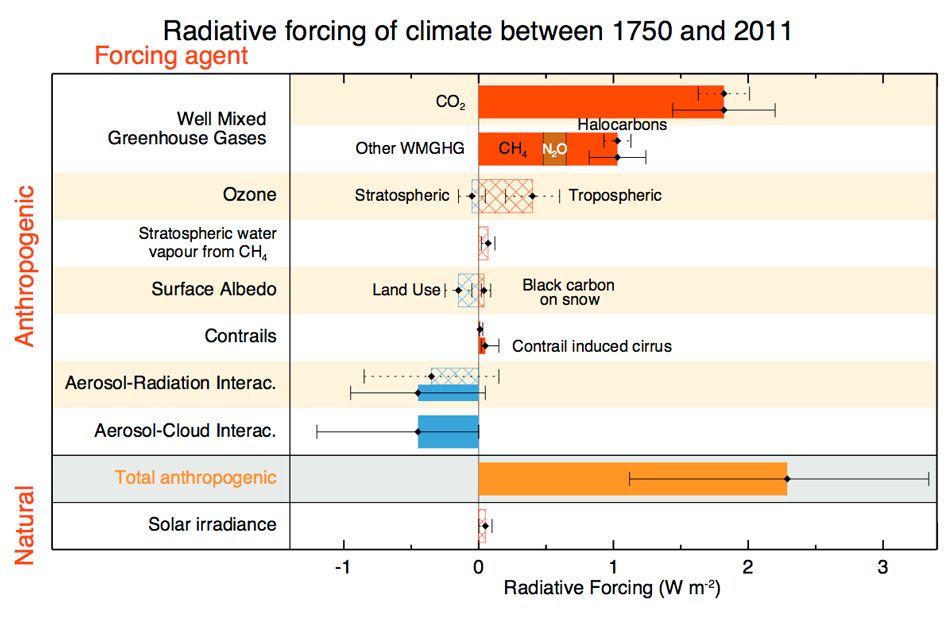



Explained Greenhouse Gases Mit News Massachusetts Institute Of Technology




Companies Responsible For Two Thirds Of Historical Greenhouse Gas Emissions Stacker



Greenhouse Gases The Environment




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




What Are The Main Man Made Greenhouse Gases Environment The Guardian
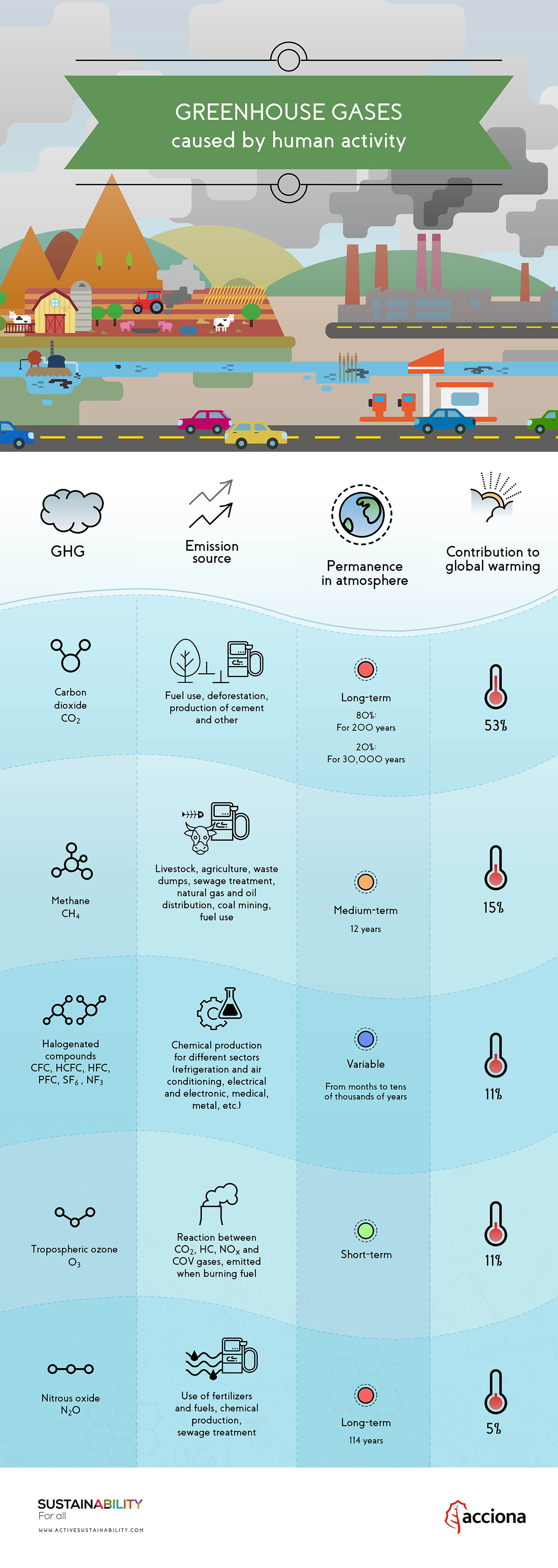



How Do Greenhouse Gases Contribute To Global Warming
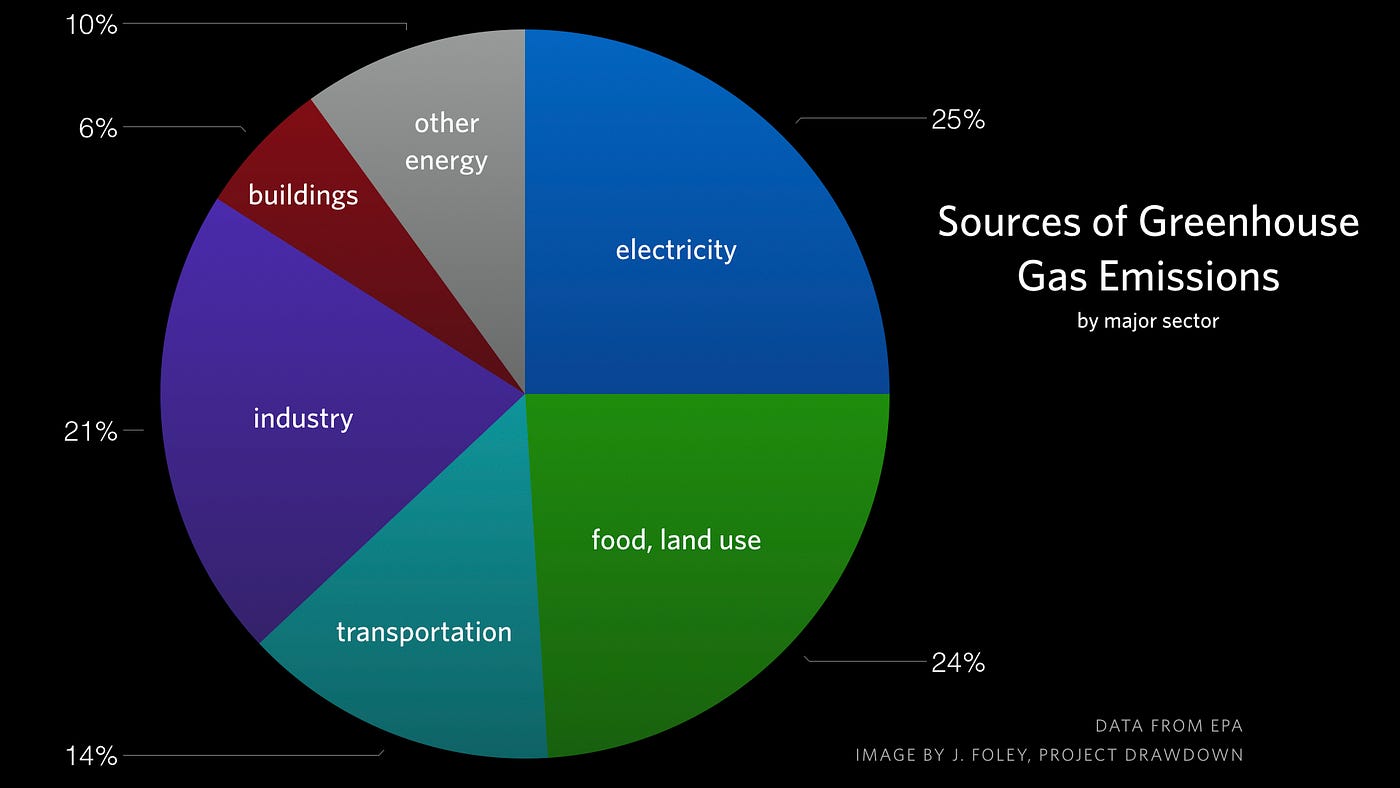



Major Causes Of Climate Change Globalecoguy Org




What Is Global Warming Live Science




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
コメント
コメントを投稿